

Determine the Observation Level of a Data Set.Creating a Variable with Group Calculations.In order to determine that, it is necessary to perform the fixed effects model in the next article. However, the results do not indicate if the randomness of this random effect model is correct and if it provides the effect set of solution.

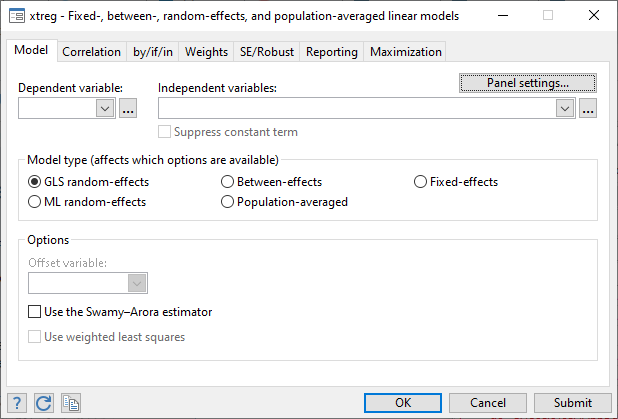
The overall random effects model looks fine and indicates that the relationship between concerned variables as significant. The above results show that the model takes care of the problem of heteroscedasticity Also the variable interest does not appear to be significantly different from the previous model. Figure 5: Results of the GLS random effect model in STATA The results of the above GLS random effect model will appear. Figure 4: Conducting random effect GLS model in STATA Here select the dependent and independent variables. xtrc EBIT LTD Int Figure 3: STATA pathway for random GLS model
Although non-normal data in case of panel regression does not have any direct impact when observations are above 83, it may have some indirect impacts. Since the data set is not normal, there are several implications in the random effect model. The rho value is 0.8516 which indicates the individual effects of cross-sections are 0.8%.The R square value also indicates the goodness of fit equals 68% which is significantly large.The coefficients of independent variable LDT and INT are significant with the p-value less than 0.05.In the above results, both the independent variables have significant effects on the dependent variable EBIT. Figure 1: Result of the random effect model in STATA for panel data analysis “re” represents the random effects for the above panel data regression. These are the variables in the order of dependent and independent variables. In the above syntax, “xtreg” represents the command Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT), Long Term Debt (LTD) and Interest payments (INT). Use the below command to start with random effect panel data analysis: xtreg EBIT LTD Int, re Since no joint or alternative effect appears in regression results, generate the effect estimates. Therefore internalise the effects of different cross sections (in this case, 30 firms) as random effects in the regression equation. On the other hand, the error terms represent random deviations of individual intercepts from the mean value. In a random effect model, the intercepts in the regression equation represent the mean values of cross-sectional intercepts. There are two ways to conduct panel data regression random effects model and fixed effect model. Therefore the present article intends to introduce to the concept of random effect model in STATA. Therefore pooled regression is not the right technique to analyze panel data series. It is also due to the fact that inclusion of too many dummies can lead to consequent loss of degrees of freedom. Therefore pooled regression is not a favourable technique for the panel data sets. The results revealed that the joint hypothesis of dummies reject the null hypothesis that these companies do not have any alternative or joint effects.
FIXED EFFECT STATA HOW TO
The p revious article (Pooled panel data regression in STATA) showed how to conduct pooled regression analysis with dummies of 30 American companies. Saptarshi Basu Roy Choudhury and Priya Chetty on October 31, 2018


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
